Tel
0577-62795555
Tel
0577-62795555
Electrical Cable Gland Types And Sizes
Consider cable gland in China, the buyer needs to know the cable AWG and which apply to cable gland datasheet. There are different types of cable gland,but generally PG and M type for different international tech standard. PG is Germany standard most accept in EU. M is a common standard under EN60432.
eg, pg 11 gland, PG represent Germany standard,11 represent code of inside diameter transfer as 18.6mm, also the max cable diameter 5-10mm.M24,24 directly represent insider diameter as 24mm, max cable diameter 10-12mm.
If detail specifications, like m32 cable gland(18-25) and M32(13-20), all share 32mm inside diameter, but one can apply cable diameter 18-25mm, other is 13-20mm which also size is much smaller.
Hont Cable Glands Features
Cable Strain Relief: Cable glands provide strain relief to prevent the cable from being pulled or twisted, which can damage the wires inside.
Sealing: Many cable glands are designed to provide a secure seal against dust, moisture, and other environmental elements. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the electrical connections and preventing corrosion.
IP Rating: Ingress Protection (IP) ratings indicate the level of protection against solids and liquids. Cable glands may have specific IP ratings to ensure they are suitable for particular environmental conditions.
Temperature Resistance: Cable glands may have temperature ratings to ensure they can withstand the operating temperatures in their intended applications without degradation.
Multiple Cable Entry Points: Some cable glands are designed to accommodate multiple cables, providing a single point of entry for several wires. This can help organize and manage cables more efficiently.
Cable Glands Applications
Industrial Environments: Cable glands are widely used in industrial settings to connect and secure cables in machinery, control panels, and other equipment. They help protect the electrical connections from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and vibrations.
Telecommunications: Cable glands are used in the telecommunications industry to secure and protect cables entering communication equipment, data centers, and cell towers. They play a role in maintaining the integrity of signal transmission.
Electrical Panels and Enclosures: In electrical panels and enclosures, cable glands are essential for ensuring a secure and organized entry point for cables. They help prevent the ingress of dust and moisture, safeguarding sensitive electrical components.
Rail and Transportation: Cable glands are used in the transportation sector, including rail and automotive applications. They secure cables in control systems, lighting, and other electrical components in vehicles and railway infrastructure.
Metal Cable Glands' Compatability for Armored Cables or Unarmored Cables
Armored Cables:
Type of Gland: When dealing with armored cables, it's common to use a specific type of metal cable gland designed to accommodate the armored structure. These are often referred to as armored cable glands or A2 cable glands.
Features: Armored cable glands typically have a design that allows them to grip and secure the armored layer of the cable. This ensures proper strain relief and protection for the cable entry point.
Unarmored Cables:
Type of Gland: For unarmored cables, standard metal cable glands can be used. These glands are designed to secure the cable without considering an additional armored layer.
Features: Standard metal cable glands provide strain relief and environmental protection for the cable entry point. They are suitable for a wide range of cable types, including those without armor.
Factors to Consider:
Cable Diameter: When selecting a metal cable gland, it's important to choose the appropriate size that matches the diameter of the cable. This ensures a proper fit and effective strain relief.
Environmental Conditions: Metal cable glands are often chosen for their durability and resistance to environmental factors. Consider the specific environmental conditions where the cables will be installed to ensure the chosen gland can provide adequate protection.
Hazardous Areas:
Explosion-Proof Glands: In environments where there is a risk of explosion, such as in some industrial settings, explosion-proof metal cable glands may be required. These glands are designed to contain any sparks or flames within the gland, preventing them from reaching the hazardous atmosphere.
Installation Practices:
Proper Installation: Regardless of whether the cable is armored or unarmored, it's essential to follow proper installation practices. This includes ensuring the correct tightening of the gland, providing effective sealing against dust and moisture, and maintaining the integrity of the cable's armor if present.
Metal Cable Glands VS Plastic Cable Glands
1. Material:
Metal Cable Glands: These are typically made from materials such as brass, stainless steel, or aluminum. The choice of metal provides durability, strength, and resistance to environmental factors.
Plastic Cable Glands: These are made from various types of plastics, such as polyamide (nylon), polyethylene, or PVC. Plastic cable glands are lightweight and may offer specific advantages in terms of chemical resistance.
2. Durability and Strength:
Metal Cable Glands: Known for their durability and high mechanical strength, metal cable glands are suitable for heavy-duty applications. They can withstand impact and physical stress.
Plastic Cable Glands: While not as mechanically robust as metal, plastic cable glands are suitable for lighter-duty applications. They are generally more lightweight and may be less resistant to physical stress.
3. Environmental Resistance:
Metal Cable Glands: Metal glands are often chosen for their resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures. Some metal glands also provide corrosion resistance.
Plastic Cable Glands: Plastic glands may offer resistance to certain environmental conditions, but they are generally not as resistant to extreme temperatures and harsh elements as metal glands.
4. Corrosion Resistance:
Metal Cable Glands: Many metal cable glands are inherently corrosion-resistant, making them suitable for outdoor and marine applications where exposure to corrosive elements is a concern.
Plastic Cable Glands: Plastic is naturally resistant to corrosion, providing an advantage in certain environments. However, plastic may degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and certain chemicals.
5. Electrical Conductivity:
Metal Cable Glands: Metal is conductive, so metal cable glands can conduct electricity. In some cases, this conductivity may need to be considered, especially in applications where electrical insulation is crucial.
Plastic Cable Glands: Plastic is an insulating material, making plastic cable glands suitable for applications where electrical conductivity must be avoided.
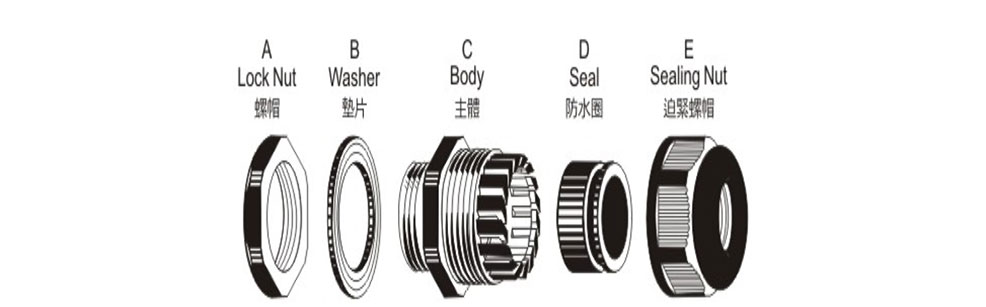
Different types of cable glands are all considered as seal tools to install the cable into the outdoor electric box, and another electric device. Engineer open hole in the electric box to attach cable, but the hole left open may bring in the water or dusty and damage the electrical appliances, electrical stuffing glands can depart as two gland body and lock nut, install from the inside and outside of the hole, seal the hole in the meantime protect the cable from edge cut. Another tech standard is cable gland should be IP68 level in GB 4208-2008/IEC 60529-2001, inside seal ring and sealing nut as components of the seal system, keep the dusty and water.
News & Topics at Hont Cable Ties